Overview:
This article guides you through resolving two common scenarios where a Windows System State restore might fail:
-
Scenario 1: Restore Failed - "Machine not rebooted"
-
Scenario 2: Restore Failed - "Metadata error"
Scenario 1: Restore Failed - "Machine not rebooted"
Once you finish restoring a Windows System State backup, the Zmanda Management Console (ZMC) may indicate a "Failed" status with the error message "Machine not rebooted."
Detailed error message:
ERROR: Machine not rebooted after previous System State Restore. Please reboot your machine. If the problem still persists, delete the ZWCTempRestore* files from "$SystemRoot\system32\config" directory. Error restoring the selected files. System State Restore Failed.Issue description:
When you restore the System State, some temporary files are created in the $SystemRoot\system32\config directory. Usually, these files are deleted when you restart your computer. However, if they persist due to operating system issues, proceeding with the restoration is not advisable. Therefore, ZMC shows the mentioned error message to alert you during the System State restoration process.
Resolution:
1. Restart the machine: This initial step often resolves the issue by automatically deleting temporary files.
2. Manually delete temporary files:
-
-
If the issue persists, identify and delete files named ZWCTempRestore* from the $SystemRoot\system32\config directory.
-
Retry the System State restore.
-
Deleting the wrong files can cause further issues. Ensure you only delete files with the correct format.
Scenario 2: Restore Failed - "Metadata error"
Upon completing the restoration of a Windows System State backup, if ZMC shows a "Failed" status with a "Metadata error" message, you'll need to download and run a script from Network Zmanda . This script ensures the correct restoration of all files. It is effective even if ZMC continues to display a "Failed" status.
Please note that a resolution for this display issue is planned for future releases.
You can find the instructions for running the script below.
Why run a script post-restore?
The script addresses two main challenges during the restoration of System State to its original location:
1. Overwriting the SOFTWARE file: During restoration, the SOFTWARE file faces difficulty in direct overwriting due to Windows locking the file. This occurs because of an associated system process. The script aids in manual overwriting, ensuring a successful restoration.
2. Metadata errors: System State restoration may encounter metadata errors, visible on the Monitor page. These errors occur when the application struggles to create hard links for certain system files. The script addresses this by identifying the failed files and creating the necessary hard links.
How to run the script:
After completing the system restore, restart your Windows machine. This ensures that any temporary files created during the restore operation are overwritten. Once the system is restarted, proceed with the following steps:
1. Download the batch script file (SystemStatePostRestore) from network.zmanda.com > Downloads > Utilities to your Windows machine. Store it in a location accessible from the OS drive.
2. Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog.
3. Type msconfig and press Enter.
4. In the System Configuration window, select the Boot menu option.
5. Under Boot options, enable Safe Boot and choose Minimal.
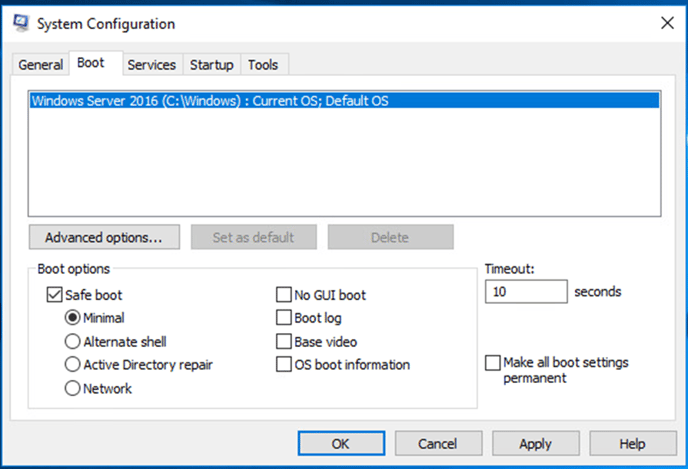
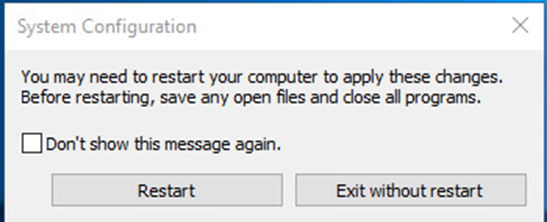
7. Select Restart.
8. After the server restarts, log in to your profile.
9. Open the command prompt.
10. Enter the command bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot.
11. Type shutdown /r /o.
Windows will restart with advanced boot menu options.
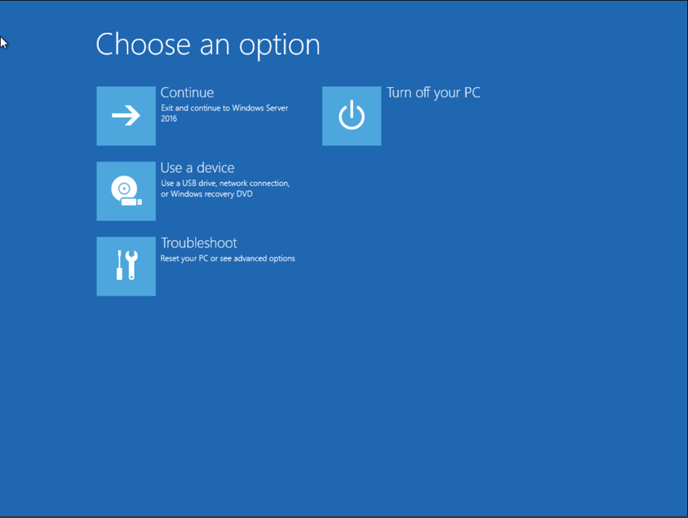
12. Choose Troubleshoot and then select Command Prompt.
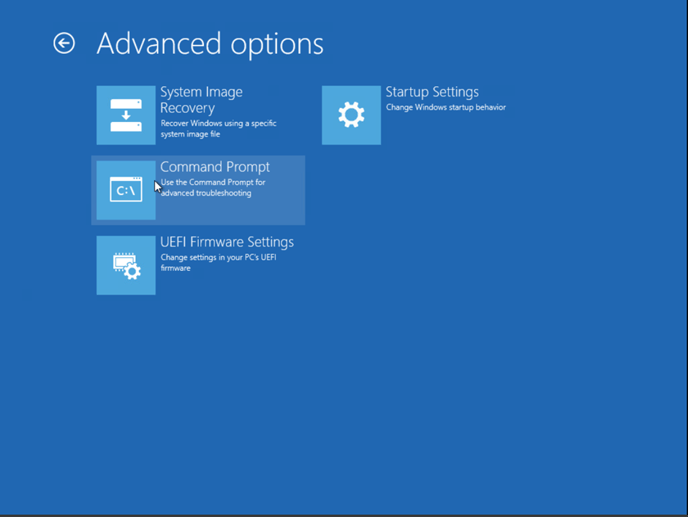
Windows will restart and load the command prompt files.
13. Choose the Administrator account to launch the command prompt.
14. Enter your password and wait for the command prompt to load.
15. After the command prompt is loaded, navigate to the directory containing the script file.
16. Run the batch script and wait for it to complete execution. This may take a couple of minutes.
17. After the batch script is executed, enter Exit and choose the Continue option in the Advanced options window to boot into Windows normally.
By following these steps, you can effectively resolve common issues leading to Windows System State restore failures, ensuring successful restoration.
